Adenosine Diphosphate
What is Adenosine Diphosphate? Explained in an easy to understand way:

What's Covered in the Video:
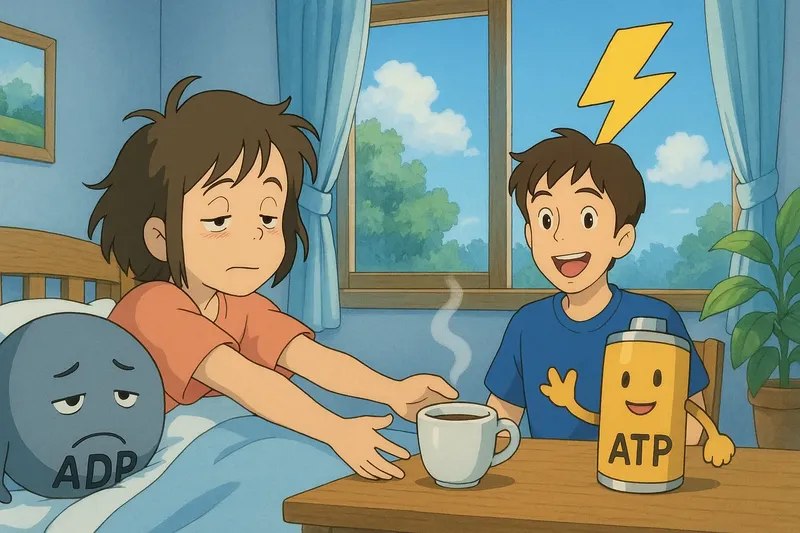
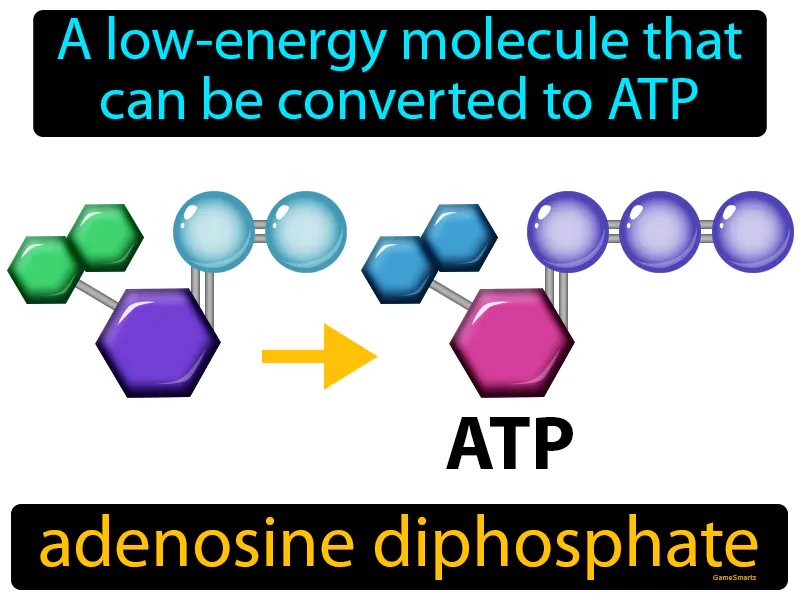
Imagine waking up in the morning feeling groggy and in need of a cup of coffee to kickstart your day. This situation is similar to how adenosine diphosphate (ADP) functions in our cells; it's like the uncharged battery that needs a boost to become ATP, the fully charged energy molecule. Just as coffee energizes you to tackle the day's tasks, converting ADP to ATP provides the energy cells need to perform essential functions, with ADP being the tired version and ATP being the alert, ready-to-go state.
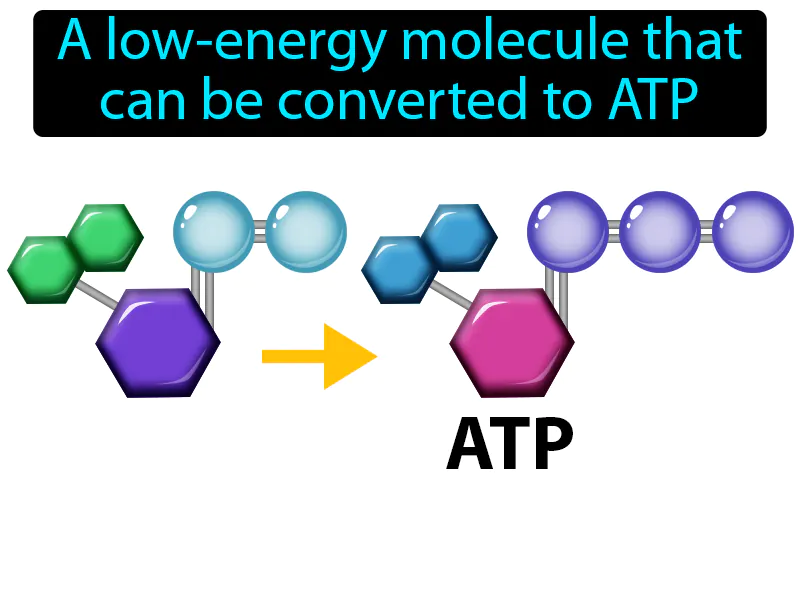
Practice Version
Adenosine Diphosphate: A low-energy molecule that can be converted to ATP. Adenosine diphosphate. Adenosine diphosphate ADP is a molecule that cells use to store and transfer energy.