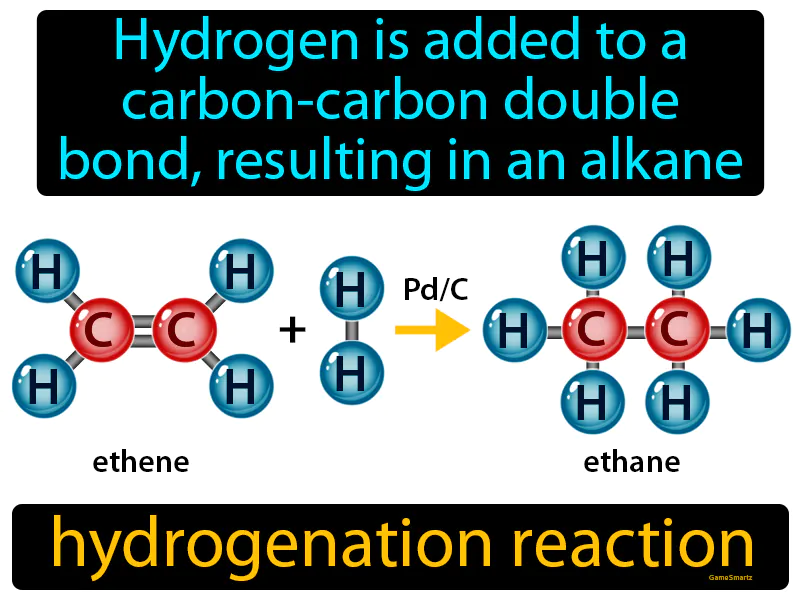
Hydrogenation Reaction
Hydrogenation Reaction: Easy to understand
Imagine you're trying to assemble a jigsaw puzzle, but there's a gap right in the middle that makes the picture incomplete. Adding hydrogen to a carbon-carbon double bond in a hydrogenation reaction is like finding the missing puzzle piece that perfectly fits the gap, turning your incomplete picture into a whole, cohesive image. Just as the puzzle piece fills in and completes the picture, hydrogen atoms attach to the double bond, converting it into a single bond and transforming the molecule from an unsaturated alkene to a saturated alkane, completing its structure and stabilizing it.
Practice Version
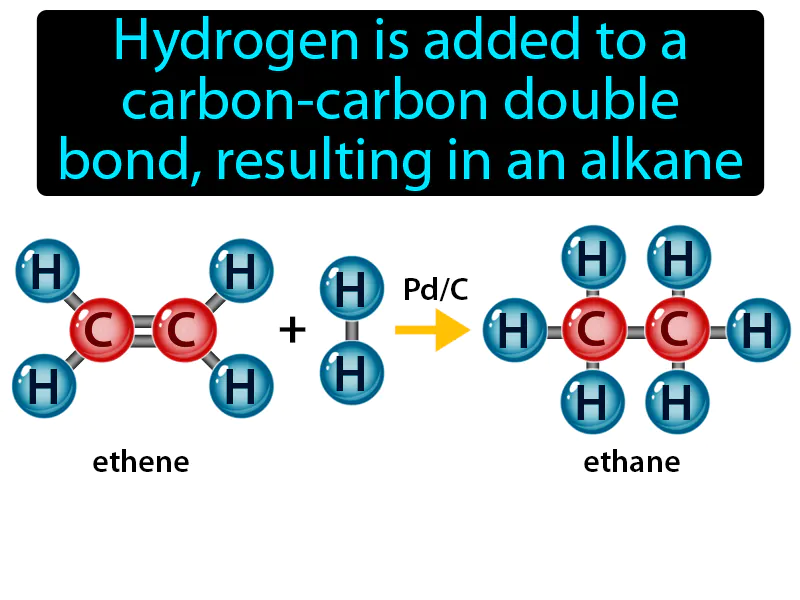
Hydrogenation Reaction: Hydrogen is added to a carbon-carbon double bond, resulting in an alkane. Hydrogenation reaction. A hydrogenation reaction is when hydrogen is added to molecules, often turning unsaturated compounds like oils into saturated ones, like fats.